Community College Partnership in Workforce
Find Your Community College
Explore the Program
Right for You
Community College Partnership in Workforce (CCPIW)

Wherever you live or work along the upper Texas Gulf Coast, you’ll find state-of-the-industry workforce training at your nearby community college! The Community College Partnership in Workforce (CCPIW), funded with a grant by ExxonMobil, consists of community colleges and school districts in the greater Houston and Texas Gulf Coast area, each providing skills training for the region’s businesses and industries.
To learn which college has a degree or certificate program in the area of your interest, click on the college’s logo appearing on the career opportunities below. Scholarships are available for technical degrees! Want to learn more about the petrochemical industry? Check out our sister site PetrochemWorks.com.
Petrochemical teaching jobs are available at member colleges of TGCCCC. Most require real job experience, and candidates can be trained to instruct students.

Meeting Energy Education Needs
The energy industry in Texas in growing rapidly as the state’s population increases and energy demands grow. To supply that energy, the industry needs more qualified employees to fill the jobs it is creating. An associate degree from a Texas Gulf Coast community college can prepare you with the right education to fill these high-paying jobs.
An aging workforce and as much as $35 billion in plant expansions along the Texas Gulf Coast means opportunities for new workers in the petrochemical industry. The industry estimates it will need to replace as many as 40% of its current workers due to retirements over the next decade, while plant expansions will need as many as 50,000 construction workers and more than 1,000 additional permanent, full-time workers.
Career Opportunities
- Analyzer Technology
- CADD
- Computer Maintenance
- Electrical Technology
- Engineering Technology
- Fieldbus Technology
- Instrumentation
- Machine Technology
- Millwrighting
- Pipefitting
- Process Technology
- Production Technology
- Supply Chain Management
- Welding

Analyzer Technology
Analyzer technicians calibrate, install, repair and perform general maintenance on instruments that provide product quality and compliance monitoring to the main control system or operator such as physical and chemical properties of products, viscosity, density, PH, and BTUs. Gas chromatographs, hydrocarbon detectors, and continuous emissions monitoring analyzer are some of the analyzer systems install and maintained by the Analyzer Technician. They must also maintain the sample systems, work closely with Technical and Operations personnel, order and stock certified sample gases for the calibration process. The data collected is extremely valuable to operations to know that the process stream is operating at the highest integrity level without any impact to the environment. In the past, most analyzers were calibrated and maintained by the instrumentation department. As the field of analyzers has grown and become so much more sophisticated, a two-year degree from a college is recommended with a certificate in instrumentation or analyzer technology.
(Source: East Harris County Manufacturing Association)
| Description | 2017 Jobs | 2027 Jobs (Projected) | Median Pay | Low Pay | High Pay |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Industrial Engineering Technician | 698 | 750 | $58,024 | $33,958 | $96,392 |
| Chemical Plant and System Operators | 2,910 | 2,692 | $66,670 | $36,092 | $91,775 |
*Jobs for recently announced petrochemical projects not yet included.
Source: QCEW (Quarterly Census of Employment and Wages) Employees, Non-QCEW Employees, Self-Employed & Extended Proprietors – EMSI 2017.3 Class of Worker. Job and wage information drawn from counties touching a 100-mile radius of Baytown, Texas.
General Requirements
Long-term on-the-job training: Occupations at this level generally require more than 12 months of on-the-job training or combined work experience and formal classroom instruction for workers to develop the skills needed for average job performance. This category includes formal and informal apprenticeships that may last up to 4 years and short- term intensive employer-sponsored training that workers must successfully complete. Individuals undergoing training are generally considered to be employed in the occupation. Includes occupations in which workers may gain experience in non-work related activities, such as professional athletes who gain experience through participation in athletic programs in academic institutions. For nuclear technicians, the requirement is completion of a degree program usually requiring at least 2 years of full-time equivalent academic work. (Source: Texas Workforce Commission)
Programs of Study
Certificate of Completion, Analytical Instrumentation – ATI1
CADD
Architectural and civil drafters prepare detailed drawings of architectural and structural features of buildings or drawings and topographical relief maps used in civil engineering projects, such as highways, bridges, and public works. Use knowledge of building materials, engineering practices, and mathematics to complete drawings. Electronic and electrical drafters prepare wiring diagrams, circuit board assembly diagrams, and layout drawings used for the manufacture, installation, or repair of electrical equipment. Mechanical drafters prepare detailed working diagrams of machinery and mechanical devices, including dimensions, fastening methods, and other engineering information.
| Description | 2017 Jobs | 2027 Jobs (Projected) | Median Pay | Low Pay | High Pay |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Architectural & Civil Drafter | 4,323 | 4,119 | $37,634 | $33,958 | $125,109 |
| Electrical & Electronics Drafter | 1,004 | 1,078 | $75,023 | $37,634 | $125,109 |
| Mechanical Drafter | 2,039 | 1,954 | $65,587 | $41,028 | $113,992 |
*Jobs for recently announced petrochemical projects not yet included.
Source: QCEW (Quarterly Census of Employment and Wages) Employees, Non-QCEW Employees, Self-Employed & Extended Proprietors – EMSI 2017.3 Class of Worker. Job and wage information drawn from counties touching a 100-mile radius of Baytown, Texas.
General Requirements
Post-secondary vocational training: Occupations at this level generally require completion of vocational school training. Some programs last only a few weeks while others may last more than a year. In some occupations, a license is needed that requires passing an examination after completion of the training. (Source: Texas Workforce Commission)
Programs of Study
- Associate of Applied Science, Computer-Aided Drafting and Design – DT2
- Associate of Applied Science, Process Piping Design – PPD2
- Certificate of Completion, Architectural Construction and Building Technology – CMT1
- Certificate of Completion, Computer-Aided Drafting and Design – TP1
- Certificate of Completion, Computer-Aided Drafting and Design, Advanced Technology – DS1
- Certificate of Completion, Mechanical Technology – MET1
- Certificate of Completion, Process Instrumentation and Electrical Design – PIED1
- Certificate of Completion, Process Piping Design – PPD1
Computer Maintenance
Computer maintenance technicians repair, maintain, program, and/or install computers, word processing systems, automated teller machines, and electronic office machines, such as duplicating and fax machines.
| Description | 2017 Jobs | 2027 Jobs (Projected) | Median Pay | Low Pay | High Pay |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Computer User Support Specialists | 13,851 | 15,915 | $54,611 | $31,870 | $92,470 |
| Computer Network Support Specialists | 3,056 | 3,477 | $70,282 | $41,819 | $118,213 |
| Computer Operators | 756 | 744 | $42,198 | $28,700 | $75,332 |
*Jobs for recently announced petrochemical projects not yet included.
Source: QCEW (Quarterly Census of Employment and Wages) Employees, Non-QCEW Employees, Self-Employed & Extended Proprietors – EMSI 2017.3 Class of Worker. Job and wage information drawn from counties touching a 100-mile radius of Baytown, Texas.
General Requirements
Some workers enter this field with a high school diploma. However, knowledge of electronics is required, so these workers commonly have a postsecondary degree or certificate. Strong communication and customer service skills are important because computer, ATM, and office machine repairers often interact with customers to figure out what needs to be repaired. (Source: Texas Workforce Commission)
Programs of Study
- Associate of Applied Science, Computer Maintenance Technology – MT2
- Certificate of Completion, Computer Maintenance Technology – MT1
- Certificate of Completion, Network Maintenance Technology – NET1
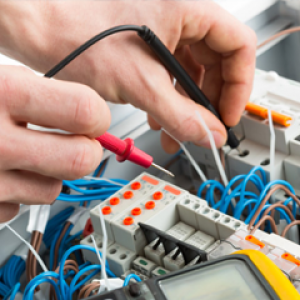
Electrical Technology
An electrician installs, maintain, tests, troubleshoots and repairs electrical equipment and other types of electrical and electronic controls on various type of equipment found in an industrial site. An electrician applies electrical theory and related knowledge, usually under direction of engineering staff to design, build, repair, calibrate and modify electrical components, circuitry, controls and machinery. To become an electrical journeyman, a person must have a certificate or Associate of Applied Science in Electrical Technology and may be required to complete a nationally certified Apprenticeship program. In the classroom, apprentices spend more than 140 hours learning how to read blueprints and craft related safety requirements. Electrical apprentices typically spend about 2,000 hours working under the supervision of experienced Journeyman electricians where they will be trained on specific craft related task and the use of personal protective equipment. Electricians will need building, mechanical, and construction knowledge.
(Source: East Harris County Manufacturing Association)
| Description | 2017 Jobs | 2027 Jobs (Projected) | Median Pay | Low Pay | High Pay |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Electrical and Electronics Engineering Technician | 4,669 | 4,754 | $58,046 | $33,380 | $108,202 |
| Electro-Mechanical Technicians | 341 | 358 | $55,940 | $36,590 | $99,147 |
| Engineering Technicians, Except Drafters, All Other | 4,669 | 4,754 | $58,046 | $33,380 | $108,202 |
| Electrical Installers and Repairers, Transportation Equipment | 270 | 299 | $65,839 | $44,080 | $96,935 |
| Electrical Repairers, Commercial and Industrial Equipment | 1,998 | 2,101 | $49,363 | $32,027 | $78,619 |
| Electrical Repairers, Powerhouse, Substation, and Relay | 242 | 276 | $60,644 | $37,342 | $101,177 |
| Electrical Equipment Installers and Repairers, Motor Vehicles | 419 | 305 | $29,662 | $16,589 | $41,835 |
| Electronic Home Entertainment Equipment Installers and Repairers | 580 | 645 | $35,356 | $21,880 | $51,594 |
*Jobs for recently announced petrochemical projects not yet included.
Source: QCEW (Quarterly Census of Employment and Wages) Employees, Non-QCEW Employees, Self-Employed & Extended Proprietors – EMSI 2017.3 Class of Worker. Job and wage information drawn from counties touching a 100-mile radius of Baytown, Texas.
General Requirements
Associate degree: Completion of the degree program usually requires at least 2 years of full-time equivalent academic work. (Source: Texas Workforce Commission)
Programs of Study
- Associate of Applied Science, Electrical Technology – IE2
- Certificate of Completion, Electrical Technology – IE1
- Certificate of Completion, Wiring Installation – EWI1
- Certificate of Completion, Electrical Construction – EC1

Engineering Technology
Engineering is a broad field, encompassing a wide variety of skills and occupations. There are chemical engineers, civil engineers, electronics and electrical engineers, systems engineers, computer hardware engineers, mechanical engineers, and many others.
| Description | 2017 Jobs | 2027 Jobs (Projected) | Median Pay | Low Pay | High Pay |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mechanical Engineering Technician | 1,994 | 2,039 | $66,568 | $32,166 | $154,555 |
| Industrial Engineering Technologist | 4,669 | 4,754 | $58,046 | $33,380 | $108,202 |
| Electronics Engineering Technologist | 4,669 | 4,754 | $58,046 | $33,380 | $108,202 |
| Mechanical Engineering Technologist | 4,669 | 4,754 | $58,046 | $33,380 | $108,202 |
| Industrial Engineering Technician | 698 | 750 | $58,024 | $33,958 | $96,392 |
| Manufacturing Engineering Technologist | 4,669 | 4,754 | $58,046 | $33,380 | $108,202 |
| Electromechanical Engineering Technologist | 4,669 | 4,754 | $58,046 | $33,380 | $108,202 |
| Electrical Engineering Technician | 4,669 | 4,754 | $58,046 | $33,380 | $108,202 |
| Electro-Mechanical Technician | 341 | 358 | $55,950 | $36,590 | $99,147 |
| Industrial Machinery Mechanic | 11,056 | 13,361 | $55,497 | $32,233 | $89,387 |
| Industrial Production Manager | 3,127 | 3,164 | $116,938 | $72,582 | $200,509 |
| Chemical Plant and System Operator | 2,910 | 2,692 | $66,670 | $36,092 | $91,775 |
*Jobs for recently announced petrochemical projects not yet included.
Source: QCEW (Quarterly Census of Employment and Wages) Employees, Non-QCEW Employees, Self-Employed & Extended Proprietors – EMSI 2017.3 Class of Worker. Job and wage information drawn from counties touching a 100-mile radius of Baytown, Texas.
General Requirements
Associate degree: Completion of the degree program usually requires at least 2 years of full-time equivalent academic work. (Source: Texas Workforce Commission)
Programs of Study
Associate of Applied Science, Manufacturing Engineering Technology – MEA2
This degree is designed for students who want to transfer to four-year schools and specialize in engineering fields related to the petrochemical industry.

Fieldbus Technology
A fairly new technology that provides a communication network for multiple field instrument signals over a single cable connection. In addition to reducing the field wiring cost some additional benefits that have been enable by this technology are remote monitoring, real-time self-diagnostics, and proactive maintenance of field devices. Instrumentation technicians maintain these systems in chemical plants, petroleum refineries, canneries, and food processing plants, as well as other businesses that control and monitor air and water environmental compliance. Instrumentation technicians perform general maintenance, test, calibrate, install, repair, and inspect monitoring devices. These industries require extremely precise measuring and monitoring equipment to regulate flow and pressure rates, keep track of production, manage power use, and ensure safety. Occupations at this level generally require more than 12 months of on-the-job training or combined work experience and formal classroom instruction. This category includes formal and informal apprenticeships that may last up to four years and short-term intensive employer-sponsored training that workers must successfully complete.(Source: East Harris County Manufacturing Association)
| Description | 2017 Jobs | 2027 Jobs (Projected) | Median Pay | Low Pay | High Pay |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Industrial Engineering Technician | 698 | 750 | $58,024 | $33,958 | $96,392 |
| Chemical Plant and System Operators | 2,910 | 2,692 | $66,670 | $36,092 | $91,775 |
*Jobs for recently announced petrochemical projects not yet included.
Source: QCEW (Quarterly Census of Employment and Wages) Employees, Non-QCEW Employees, Self-Employed & Extended Proprietors – EMSI 2017.3 Class of Worker. Job and wage information drawn from counties touching a 100-mile radius of Baytown, Texas.
General Requirements
Long-term on-the-job training: Occupations at this level generally require more than 12 months of on-the-job training or combined work experience and formal classroom instruction for workers to develop the skills needed for average job performance. This category includes formal and informal apprenticeships that may last up to 4 years and short- term intensive employer-sponsored training that workers must successfully complete. Individuals undergoing training are generally considered to be employed in the occupation. Includes occupations in which workers may gain experience in non-work activities, such as professional athletes who gain experience through participation in athletic programs in academic institutions. For nuclear technicians, the requirement is completion of a degree program usually requiring at least 2 years of full-time equivalent academic work. (Source: Texas Workforce Commission)
Programs of Study
- Certificate of Completion, Instrumentation—AT11

Instrumentation
Instrumentation technicians install, test, calibrate and perform general maintenance on some of the most sophisticated, extremely precise measuring and monitoring equipment in the world. They are highly skilled technologists. Instrumentation technicians work in refining, petrochemical and manufacturing industries. They are valuable for the control of processes and environmental compliance. Most instrument technicians become certified in a national standard. Students learn to read, analyze and produce electronic drafting documents. There is a shortage of instrument technicians in the Gulf Coast area and the shortage will only increase as many analyzer technicians retire in the next five to ten years. Employers generally give preference to candidates who have a certification or Associates of Applied Science in Instrumentation.
(Source: East Harris County Manufacturing Association)
| Description | 2017 Jobs | 2027 Jobs (Projected) | Median Pay | Low Pay | High Pay |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Industrial Engineering Technician | 698 | 750 | $58,024 | $33,958 | $96,392 |
| Chemical Plant and System Operators | 2,910 | 2,692 | $66,670 | $36,092 | $91,775 |
*Jobs for recently announced petrochemical projects not yet included.
Source: QCEW (Quarterly Census of Employment and Wages) Employees, Non-QCEW Employees, Self-Employed & Extended Proprietors – EMSI 2017.3 Class of Worker. Job and wage information drawn from counties touching a 100-mile radius of Baytown, Texas.
General Requirements
Long-term on-the-job training: Occupations at this level generally require more than 12 months of on-the-job training or combined work experience and formal classroom instruction for workers to develop the skills needed for average job performance. This category includes formal and informal apprenticeships that may last up to 4 years and short- term intensive employer-sponsored training that workers must successfully complete. Individuals undergoing training are generally considered to be employed in the occupation. Includes occupations in which workers may gain experience in non-work activities, such as professional athletes who gain experience through participation in athletic programs in academic institutions. For nuclear technicians, the requirement is completion of a degree program usually requiring at least 2 years of full-time equivalent academic work. (Source: Texas Workforce Commission)
Programs of Study
Certificate of Completion, Analytical Instrumentation – ATI1

Machine Technology
Machinists set up and operate a variety of machine tools to produce precision parts and instruments. This field includes precision instrument makers who fabricate, modify, or repair mechanical instruments. They may also fabricate and modify parts to make or repair machine tools or maintain industrial machines, applying knowledge of mechanics, mathematics, metal properties, layout, and machining procedures. Many machine shops still use the manual setting up of mills and lathes, but many have transitioned to the new CNC (computer numerical code) technology. The Gulf Coast area has a significant need for machinists. Certificates of completion or an Associates of Applied Science in Industrial Systems gives job seekers an advantage over other candidates. Knowledge of computer numerical code is a must in the modern machine shop. Occupations at this level generally require more than twelve months of on-the-job training or combined work experience and formal classroom instruction for workers to develop the skills needed for average job performance.
(Source: East Harris County Manufacturers Association)
| Description | 2017 Jobs | 2027 Jobs (Projected) | Median Pay | Low Pay | High Pay |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Structural Metal Fabricators and Fitters | 3,886 | 3,324 | $39,972 | $28,445 | $59,572 |
| Computer Numerically Controlled Machine Tool Programmers, Metal and Plastic | 627 | 639 | $60,824 | $33,784 | $83,389 |
| Drilling and Boring Machine Tool Setters, Operators, and Tenders, Metal and Plastic | 225 | 196 | $29,794 | $20,506 | $50,786 |
| Machinists | 10,029 | 9,842 | $44,838 | $29,306 | $64,378 |
| Model Makers, Metal and Plastic | 54 | 53 | $41,533 | $36,640 | $65,579 |
| Patternmakers, Metal and Plastic | 52 | 36 | $45,271 | $34,411 | $59,710 |
| Tool and Die Makers | 322 | 311 | $50,658 | $25,712 | $72,671 |
*Jobs for recently announced petrochemical projects not yet included.
Source: QCEW (Quarterly Census of Employment and Wages) Employees, Non-QCEW Employees, Self-Employed & Extended Proprietors – EMSI 2017.3 Class of Worker. Job and wage information drawn from counties touching a 100-mile radius of Baytown, Texas.
General Requirements
Long-term on-the-job training: Occupations at this level generally require more than 12 months of on-the-job training or combined work experience and formal classroom instruction for workers to develop the skills needed for average job performance. This category includes formal and informal apprenticeships that may last up to 4 years and short- term intensive employer-sponsored training that workers must successfully complete. Individuals undergoing training are generally considered to be employed in the occupation. Includes occupations in which workers may gain experience in non-work activities, such as professional athletes who gain experience through participation in athletic programs in academic institutions. (Source: Texas Workforce Commission)
Programs of Study
- Certificate of Completion, Industrial Systems – Machinist – MC1

Millwrighting
A millwright is a craftsman who can install, repair and perform maintenance on rotating and fixed equipment, such as pumps, turbines and compressors. A millwright knows how to take precision measurements on equipment, use laser alignment tools, remove/install mechanical and gas seals, remove/install bearings of all types. Millwrights install, dismantle, or move machinery according to layout plans, blueprints or other drawings. With the Gulf Coast area economy going strong there’s a significant need for millwrights. Certificates of completion or Associates of Applied Science in Industrial Systems–Technician, Machinist, or Millwright give a job seeker an advantage over other candidates. Occupations at this level generally require more than twelve months of on-the-job training or combined work experience and formal classroom instruction for workers to develop the skills needed for average job performance.
(Source: East Harris County Manufacturers Association)
| Description | 2017 Jobs | 2027 Jobs (Projected) | Median Pay | Low Pay | High Pay |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Millwrights | 1,183 | 1,440 | $47,503 | $28,952 | $77,944 |
| Milling and Planing Machine Setters, Operators, and Tenders, Metal and Plastic | 945 | 737 | $46,263 | $29,104 | $64,729 |
*Jobs for recently announced petrochemical projects not yet included.
Source: QCEW (Quarterly Census of Employment and Wages) Employees, Non-QCEW Employees, Self-Employed & Extended Proprietors – EMSI 2017.3 Class of Worker. Job and wage information drawn from counties touching a 100-mile radius of Baytown, Texas.
General Requirements
Long-term on-the-job training: Occupations at this level generally require more than 12 months of on-the-job training or combined work experience and formal classroom instruction for workers to develop the skills needed for average job performance. This category includes formal and informal apprenticeships that may last up to 4 years and short- term intensive employer-sponsored training that workers must successfully complete. Individuals undergoing training are generally considered to be employed in the occupation. Includes occupations in which workers may gain experience in non-work activities, such as professional athletes who gain experience through participation in athletic programs in academic institutions. (Source: Texas Workforce Commission)
Programs of Study
- Associate of Applied Science, Industrial Systems Technician – IS2
- Certificate of Completion, Industrial Systems – Machinist – MC1
- Certificate of Completion, Industrial Systems – Millwright – MW1

Pipefitting
Pipefitters and steamfitters typically layout, assemble, install, alter, and repair pipelines or pipe systems that carry water, steam, air, lubrication, or other liquids or gases for industrial production and process systems. Additionally pipefitters apply pipe system knowledge and blueprint reading capability to select pipe size and type, related equipment and materials such as pipe supports, hangars, and hydraulic supports systems according to required specifications. Includes sprinklerfitters.
| Description | 2017 Jobs | 2027 Jobs (Projected) | Median Pay | Low Pay | High Pay |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pipelayers | 1,675 | 1,912 | $32,193 | $25,951 | $50,894 |
| Plumbers, Pipefitters, and Steamfitters | 14,396 | 16,838 | $48,877 | $31,488 | $72,694 |
| Helpers – Pipelayers, Plumbers, Pipefitters, and Steamfitters | 2,990 | 3,415 | $33,159 | $25,666 | $51,357 |
*Jobs for recently announced petrochemical projects not yet included.
Source: QCEW (Quarterly Census of Employment and Wages) Employees, Non-QCEW Employees, Self-Employed & Extended Proprietors – EMSI 2017.3 Class of Worker. Job and wage information drawn from counties touching a 100-mile radius of Baytown, Texas.
General Requirements
Long-term on-the-job training: Occupations at this level generally require more than 12 months of on-the-job training or combined work experience and formal classroom instruction for workers to develop the skills needed for average job performance. This category includes formal and informal apprenticeships that may last up to 4 years and short- term intensive employer-sponsored training that workers must successfully complete. Individuals undergoing training are generally considered to be employed in the occupation. Includes occupations in which workers may gain experience in non-work activities, such as professional athletes who gain experience through participation in athletic programs in academic institutions. (Source: Texas Workforce Commission)
Programs of Study
- Associate of Applied Science, Pipefitting Technology – PF2
- Certificate of Completion, Pipefitting Technology – PF1
- Certificate of Completion, Pipefitter Helper – PH1

Process Technology
Process technicians and operators manage and control the flows, levels, temperatures, pressures, and analytical variables in refineries and petro- chemical facilities to make the fuels, chemicals, and plastics that make modern society possible. Occupations at this level generally require more than twelve months of on-the-job training or combined work experience and formal classroom instruction. This category includes formal and informal apprenticeships that may last up to four years and short- term intensive employer-sponsored training that workers must success- fully complete. Manager-level positions generally require completion of a degree program consisting of at least four years but not more than five years of full-time equivalent academic work.
(Source: Texas Workforce Commission)
| Description | 2017 Jobs | 2027 Jobs (Projected) | Median Pay | Low Pay | High Pay |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Machinery Maintenance Workers | 2,822 | 3,092 | $42,733 | $27,245 | $68,269 |
| General Maintenance and Repair Workers | 2,822 | 3,092 | $42,733 | $27,245 | $68,269 |
| Industrial Machinery Mechanics | 11,056 | 13,361 | $55,497 | $32,233 | $89,387 |
| Chemical Equipment Operator and Tender | 8,209 | 7,649 | $68,143 | $33,497 | $99,781 |
| Industrial Engineering Technician | 698 | 750 | $58,024 | $33,958 | $96,392 |
| Industrial Production Managers | 3,127 | 3,164 | $116,938 | $72,582 | $200,509 |
*Jobs for recently announced petrochemical projects not yet included.
Source: QCEW (Quarterly Census of Employment and Wages) Employees, Non-QCEW Employees, Self-Employed & Extended Proprietors – EMSI 2017.3 Class of Worker. Job and wage information drawn from counties touching a 100-mile radius of Baytown, Texas.
General Requirements
Moderate- or long-term on-the-job training: Occupations at this level generally require more than 12 months of on-the-job training or combined work experience and formal classroom instruction for workers to develop the skills needed for average job performance. This category includes formal and informal apprenticeships that may last up to 4 years and short- term intensive employer-sponsored training that workers must successfully complete. Individuals undergoing training are generally considered to be employed in the occupation. Includes occupations in which workers may gain experience in non-work activities, such as professional athletes who gain experience through participation in athletic programs in academic institutions. Manager-level positions generally require completion of a degree program consisting of at least 4 years but not more than 5 years of full-time equivalent academic work. (Source: Texas Workforce Commission)
Programs of Study
- Associate of Applied Science, Process Technology – PT2
- Associate of Applied Science, Manufacturing Engineering Technology – MEA2
- Associate of Applied Science, High School Articulation – PT2
- Certificate of Completion, Process Technology – PT1

Production Technology
Production technicians perform, plan, direct, or coordinate the work activities and resources necessary for manufacturing products in accordance with cost, quality, and quantity specifications.
| Description | 2017 Jobs | 2027 Jobs (Projected) | Median Pay | Low Pay | High Pay |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Industrial Production Managers | 3,127 | 3,164 | $116,938 | $72,582 | $200,509 |
| Manufacturing Production Technician | 4,669 | 4,754 | $58,046 | $33,380 | $108,202 |
| Production Workers | 12,814 | 12,687 | $27,076 | $18,266 | $37,260 |
| Industrial Machinery Mechanic | 11,056 | 13,361 | $55,497 | $32,223 | $89,387 |
*Jobs for recently announced petrochemical projects not yet included.
Source: QCEW (Quarterly Census of Employment and Wages) Employees, Non-QCEW Employees, Self-Employed & Extended Proprietors – EMSI 2017.3 Class of Worker. Job and wage information drawn from counties touching a 100-mile radius of Baytown, Texas.
General Requirements
Some workers enter this field with a high school diploma. However, special training is often required, so these workers commonly have a postsecondary degree or certificate. Manager-level positions generally require a degree program consisting of at least 4 years but not more than 5 years of full-time equivalent academic work. (Source: Texas Workforce Commission)
Programs of Study
- Associate of Applied Science, Manufacturing Engineering Technology – MAET2

Supply Chain Management
Logistics technicians/managers: plan, direct, or coordinate transportation, storage, or distribution of goods and services; create strategies and develop forecasting plans to keep sufficient inventory by working as the principal liaison between company and supplier; and verify goods are reaching their destination in a timely manner. Supply chain managers: provide guidance on selection of suppliers; analyze pricing trends that may affect the timing of purchases; organize the activities involved with the distribution of the goods that a company provides to its customers; and manage the process of locating and securing materials.
(Source: East Harris County Manufacturers Association)
| Description | 2017 Jobs | 2027 Jobs (Projected) | Median Pay | Low Pay | High Pay |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Transportation, Storage, and Distribution Managers | 2,586 | 2,878 | $98,386 | $61,894 | $181,606 |
| All Other Managers | 13,150 | 16,211 | $63,053 | $41,786 | $94,077 |
| Logisticians | 4,372 | 4,696 | $82,881 | $46,880 | $143,579 |
*Jobs for recently announced petrochemical projects not yet included.
Source: QCEW (Quarterly Census of Employment and Wages) Employees, Non-QCEW Employees, Self-Employed & Extended Proprietors – EMSI 2017.3 Class of Worker. Job and wage information drawn from counties touching a 100-mile radius of Baytown, Texas.
General Requirements
Completion of the degree program for manager-level jobs generally requires at least 4 years but not more than 5 years of full-time equivalent academic work. Other positions may only require a certificate of completion. (Source: Texas Workforce Commission)
Programs of Study
- Associate of Applied Science, Logistics and Supply Chain Management – LOG2
- Certificate of Completion, Logistics and Supply Chain Management – LOG1

Welding
Welders use hand-welding or flame-cutting equipment to weld or join metal components or to fill holes, indentations, or seams of fabricated metal products. The process of welding uses either electricity or various gasses to create high temperatures that bond metals. Welders may also be required to flame cut or cold cut metal based on blueprints and/or isometric drawings to construct new pipe or structural steel systems for process systems and unit infrastructure components. Flame cutting may also be required for equipment demo prior to new construction of new equipment. The skill level varies between different types of welding depending on the metallurgy and process required to complete a reliable weld.
| Description | 2017 Jobs | 2027 Jobs (Projected) | Median Pay | Low Pay | High Pay |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Welders, Cutters, Solderers, and Brazers | 18,226 | 18,304 | $45,800 | $31,016 | $74,297 |
| Welding, Soldering, and Brazing Machine Setters, Operators, and Tenders | 1,109 | 947 | $42,532 | $29,294 | $60,635 |
*Jobs for recently announced petrochemical projects not yet included.
Source: QCEW (Quarterly Census of Employment and Wages) Employees, Non-QCEW Employees, Self-Employed & Extended Proprietors – EMSI 2017.3 Class of Worker. Job and wage information drawn from counties touching a 100-mile radius of Baytown, Texas.
General Requirements
Post-secondary vocational training: Occupations at this level generally require completion of vocational school training. Some programs last only a few weeks while others may last more than a year. In some occupations, a license is needed that requires passing an examination after completion of the training. (Source: Texas Workforce Commission)
Programs of Study
- Associate of Applied Science, Welding Technology – WE2
- Certificate of Completion, Welding Technology – WE1
- Certificate of Completion, Welding Inspection Technology – WI1
Hear What Our Students Have to Say!
-
At the College of Mainland, I received tons of support, education, and experience through local hospitals and specialized clinics. Their SIM lab is incredible because it is the closest reality that you're going to get and I feel very prepared in the future of any critical care situation.
Nursing Student, College of the Mainland
-
I love the care that goes into community colleges and that community is usually their focus. The first time I set foot on Alvin Community College campus, I felt at home and welcomed instead of just another student.
ADN Student, Alvin Community College